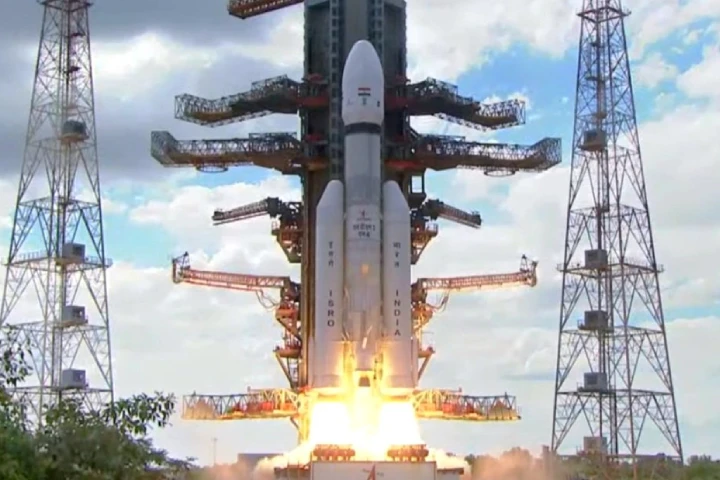
India’s successful launch of the Chandrayaan-3 mission on July 14, 2023, marks a significant milestone in space exploration. This mission represents India’s second attempt to softly land a robotic spacecraft on the Moon, and if successful, it will establish India as the fourth country to achieve this feat.
Beyond the scientific and technological advancements, the Chandrayaan-3 mission will bolster India’s position in space leadership. Here are some of the ways in which Chandrayaan-3 will contribute to India’s enhanced global standing:
Elevating India’s stature as a spacefaring nation
The triumph of Chandrayaan-3 will exemplify India’s growing technological prowess and unwavering commitment to space exploration. India also strengthens its reputation as a leader in space missions, making it a more appealing partner for international collaborations.
Indian satellites are providing services to numerous countries around the world. These include:
United States: India’s earth observation satellites from the Cartosat series, have provided valuable data to the United States for applications like mapping, urban planning, disaster management, and environmental monitoring.
France: India’s SARAL satellite, launched in partnership with the French Space Agency (CNES), has been used for oceanographic and climate studies.
United Kingdom: India’s satellites have aided in remote sensing and earth observation activities, enabling applications like disaster management, agriculture, and weather forecasting.
Israel: India’s ISRO and Israeli space agency ISA have collaborated on satellite projects. India launched Israel’s TECSAR satellite, used for advanced imaging and reconnaissance purposes.
ASEAN countries: India has extended its space services to several countries in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations region for remote sensing, disaster management, and communication needs of ASEAN member countries.
Africa: India has collaborated with multiple African countries, offering satellite-based services for various purposes, including telecommunication, broadcasting, and remote sensing. India’s GSAT satellites have been utilized to expand communication infrastructure and enhance connectivity in African nations.
India aims at contributing to the development and growth of other nations through its advancements in space technology and services.
Driving job creation and economic growth
The Chandrayaan-3 mission will generate employment opportunities directly and indirectly within the space sector. This surge in job creation will not only boost economic growth but also contribute to the development of a more skilled workforce.
Inspiring the next generation of scientists and engineers
Chandrayaan-3’s mission will serve as an inspiration for budding scientists and engineers in India. This encouragement will ensure that India continues to lead in space exploration, fostering future innovation and discoveries.
India has made significant contributions to space innovation. Some notable space innovations from India include:
- Affordable Space Launch: India developed the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), known for its cost-effectiveness and reliability in launching satellites into space.
- Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan): India’s Mangalyaan mission to Mars showcased the country’s capability to achieve interplanetary missions at a fraction of the cost compared to other nations.
- Reusable Launch Vehicle Technology Demonstrator: India has been working on developing reusable launch vehicle technology to reduce the cost of access to space.
- Remote Sensing and Earth Observation: India’s satellites, including those in the Cartosat series, have enabled remote sensing and Earth observation for various applications like mapping, disaster management, and agricultural monitoring.
- Navigation System: India’s indigenous navigation system, NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation), provides precise positioning and timing services for navigation and disaster management purposes.
- Space-based Solar Power: India has been researching space-based solar power systems, which have the potential to provide renewable energy solutions with continuous power generation.
These innovations reflect India’s commitment to leveraging space technology for societal benefits, cost-effectiveness, and expanding its capabilities in space exploration and applications.
Granting India a prominent role in international space discussions
The successful launch of Chandrayaan-3 will empower India to actively shape the future of space exploration at a global scale. India has collaborated with other nations and space agencies including:
- United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UN COPUOS): India has been an active participant in UN COPUOS meetings, contributing to discussions on space policy, international cooperation, and the peaceful uses of outer space.
- International Astronautical Congress (IAC): India has regularly participated in the IAC, a premier global space event, where experts, scientists, and policymakers discuss space-related advancements and future missions.
- International Lunar Decade (ILD): India has engaged in discussions regarding the ILD, a global initiative aimed at fostering collaboration for lunar exploration, research, and utilization.
- International Space Exploration Coordination Group (ISECG): India has contributed to the ISECG, an international forum where space agencies coordinate their efforts for future space exploration missions.
- Global Multilateral Space Diplomacy: India has engaged in diplomatic dialogues and negotiations with various countries to promote international cooperation, space-based services, and peaceful uses of outer space.
India’s active participation in these international space discussions highlights its commitment to collaborative efforts, knowledge-sharing, and contributing to the global space community’s collective goals and aspirations.
Overall, the Chandrayaan-3 mission holds the potential to enhance India’s global position in multiple ways. It will solidify India’s status as a spacefaring nation, stimulate job creation and economic growth, inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers, and enable active participation in international space discussions.
Chandrayaan-3 mission will yield several indirect advantages
For instance, it will elevate India’s global profile, attracting foreign investments, again speeding up India’s race to being the fastest growing economy in the world and fulfilling Prime Minister Modi’s bold vision to make India a $10 trillion economy by 2030. The mission also has the potential to promote scientific education within India, by making India a sought after destination for space science study, even attract admissions from foreign students.
Conclusion
The successful launch of Chandrayaan-3 represents a remarkable milestone that bolsters India’s global position. The mission is a testament to the dedication and hard work of the ISRO team, instilling a sense of pride within the Indian nation. With confidence, we can anticipate that the Chandrayaan-3 mission will propel India toward even greater accomplishments in space exploration in the years to come.